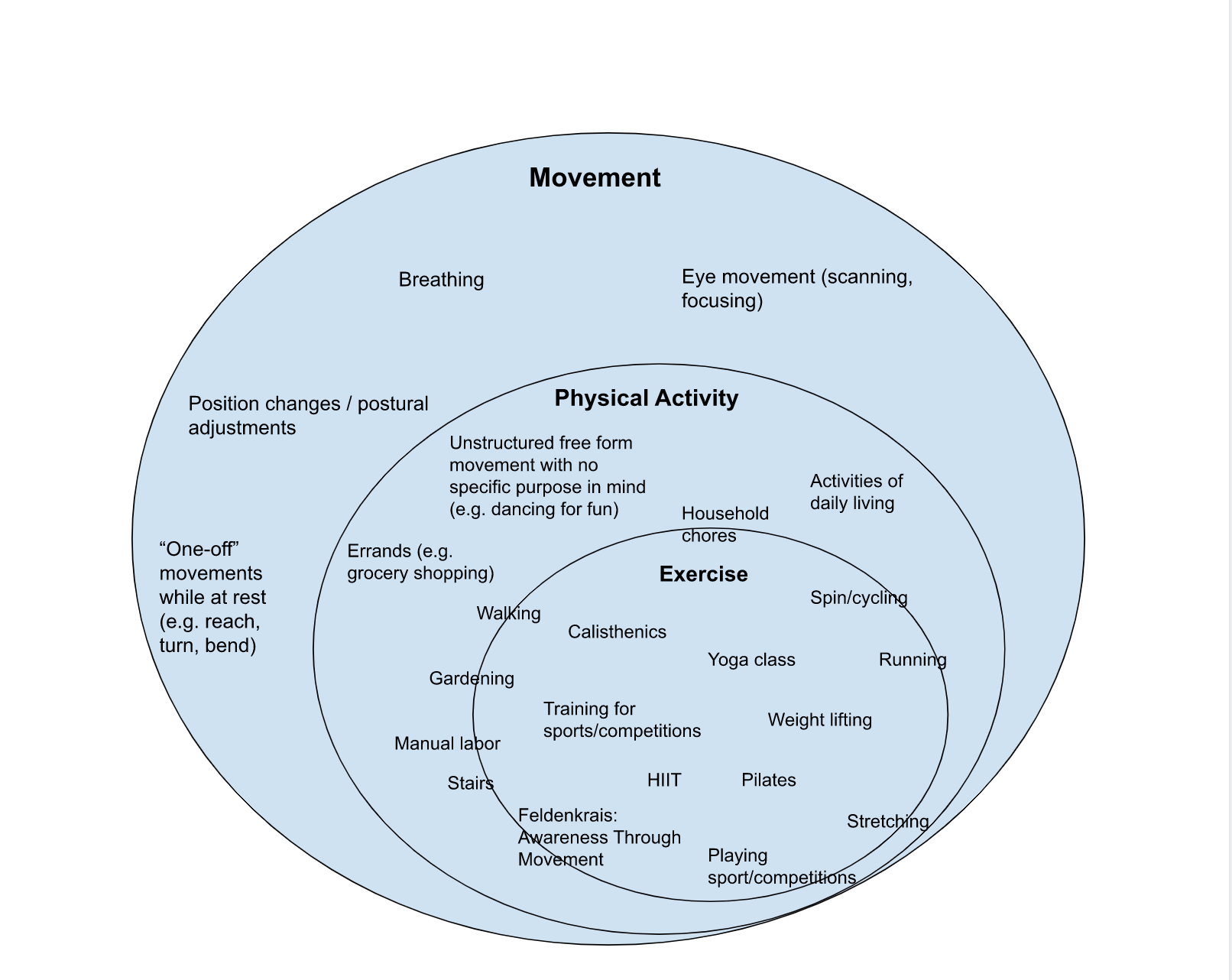
What is our core, what does it mean to have a strong core, and what are the best methods to achieve this?
Many of us associate the idea of having a strong core with the ability to stay active and independent as we age, maintain our balance, avoid injury, ease back pain, or perhaps maintain a trim waistline.
Although the idea of core strength is popular and highly sought after, what we are really after is core responsiveness: how efficient and with how much precision are our core muscles able to respond to the needs of our environment and our intentions. In other words, how well are our bodies able to do what we want them to do in a given situation?
This responsiveness depends on our neuromuscular system- the intricate connections between our brain, spinal cords, and muscles. It is crucial that this responsiveness includes all of the tiny muscles that connect each of our vertebrae, which are vital for dynamic stability, proprioception, and the ability to "change shapes" depending on the needs of the situation.
In the world of traditional physical therapy and fitness, the idea of core strength is often reduced to "core stability", and focuses on the ability to brace and hollow the abdomen. The general notion is that we must be able to keep our core very tight and rigid during movement, lest we injure our spines. This rigid stability utilizes the large, long muscles that travel up and down the spine, neglecting the tiny muscles in between each vertebrae. This is not how we function as human beings!
As we live in a three-dimensional world, our bodies need to be able to efficiently change shapes based on the situation we are in. By only training ourselves to keep our cores tight and thus restricting movement, we are behaving in a linear manner that is not conducive to our dynamic, three-dimensional world. Although this type of core engagement can be helpful in some situations (perhaps if a pet or a baby decided to crawl on our stomach!), far more often this approach is selling ourselves short and could actually put us at a higher risk of injury, pain, or limited function.
Consider the example of a stack of blocks connected by elastic bands as referenced in our Ehlers Danlos blog post, illustrating the difference between segmental vs. rigid core responsiveness. The traditional approach to core stability is similar to the example in which the blocks are connected only by four long rubber bands, in which the vertebrae (like the tower of blocks) are undifferentiated and controlled using the large, long muscles of the spine. This would neglect the small muscles of the spine that allow us to move with efficiency, fluidity, and balance. Our approach at The Wellness Station reflects the example in which the tower is connected by smaller rubber bands in between each block, allowing the structure to form a variety of complex shapes and forms, representing segmental spinal responsiveness.
Our core is our spine- we need to be able to move our spine in the three dimensions. Flexion and extension, side bending, and rotation. Each of our many vertebrae are capable of movement, and our deep spinal muscles (including the transversospinales and the segmental muscles) allow this movement.
By engaging in mindful movement practices to target these muscle groups, we can strengthen our mind-body connection to these areas, thereby improving responsiveness of our core.
This is truly what core strength is- our ability to move our spines into different shapes efficiently, mindfully, and powerfully depending on our intention and the circumstance we find ourselves in.
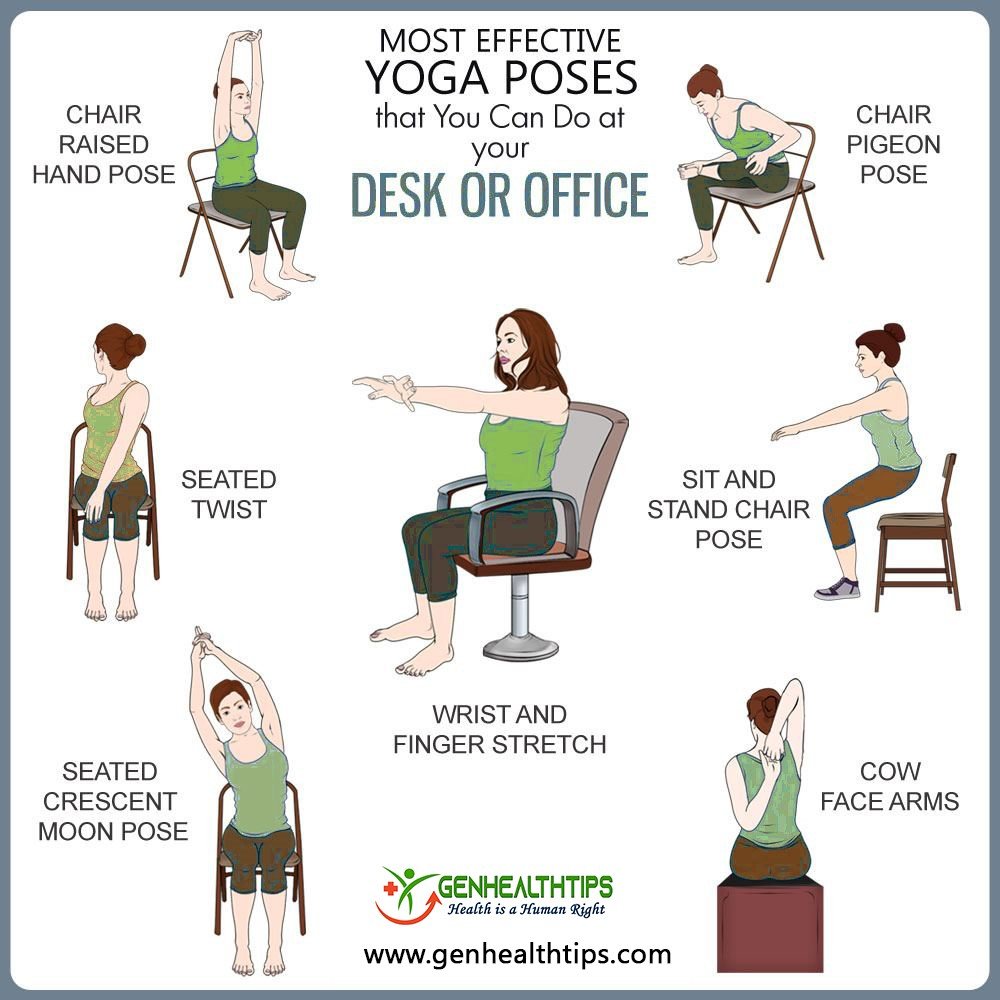
Here are some examples of mindful movement drills that engage the body in three-dimensions, and target segmental movement of the spinal column. Enjoy!
Written by Jacob Tyson, DPT - Physical Therapist, Yoga Instructor and The Wellness Station Team